If you’re a developer or a power user venturing into the world of macOS software development, you’ve likely encountered a pivotal moment in your workflow: a terminal command fails, and you’re met with the message, xcode-select: note: install requested for command line developer tools. This prompt is not an error; it is an invitation—a gateway to unlocking the full potential of your Mac for coding, compiling, and building software. This guide will demystify this message, explain why it appears, and provide you with a comprehensive roadmap for not only installing the necessary tools but also understanding and managing them for a seamless development experience.
Understanding the Gatekeeper: What This Prompt Means
At its core, the message xcode-select: note: install requested for command line developer tools is your Mac’s way of telling you that a software tool you just tried to use relies on a fundamental suite of developer components that are not currently present on your system.
The key player here is the xcode-select command. This is a macOS utility that manages the active developer directory. This directory is the path where the system looks for all its core development tools like git, clang, make, gcc, and many others. When you type a command like git clone or make into the terminal for the first time, the system checks the active developer directory for these tools. If it finds nothing (because the tools aren’t installed), it triggers the xcode-select utility to request the installation. This elegant system ensures developers get the tools they need, on-demand.
There are two primary packages that can satisfy this request:
The Command Line Tools (CLT) Package: This is a lean, standalone package that contains the essential compilers, debuggers, and utilities without the massive overhead of the full Xcode IDE. It’s the fastest and most common solution for most users.
The Full Xcode Application: This is Apple’s complete Integrated Development Environment, available for free on the Mac App Store. It includes the Command Line Tools within it, along with a graphical editor, simulators, and instruments for profiling. It is several gigabytes larger.
For most developers who work primarily in the terminal or use other IDEs like VS Code or JetBrains products, installing the standalone Command Line Tools package is perfectly sufficient.
Why You’re Seeing This Message: Common Triggers
The prompt is your system’s response to a missing dependency. You will encounter it when you attempt to run any command that depends on the Apple developer toolchain. Common triggers include:
Using Version Control: Commands like
git,svn, orhgare part of the CLT.Compiling Code: Using compilers like
gccorclang, or build tools likemakeorcmake.Installing Software via Package Managers: Many popular package managers for macOS, such as Homebrew, MacPorts, or even
pipfor Python, require the CLT to compile and install software from source.Running Scripts or Tools: Many open-source projects and automation scripts have underlying dependencies on these core tools.
Method 1: The Direct Installation (Recommended)
The simplest and most user-friendly way to resolve the xcode-select: note: install requested for command line developer tools message is to let the system itself handle the installation.
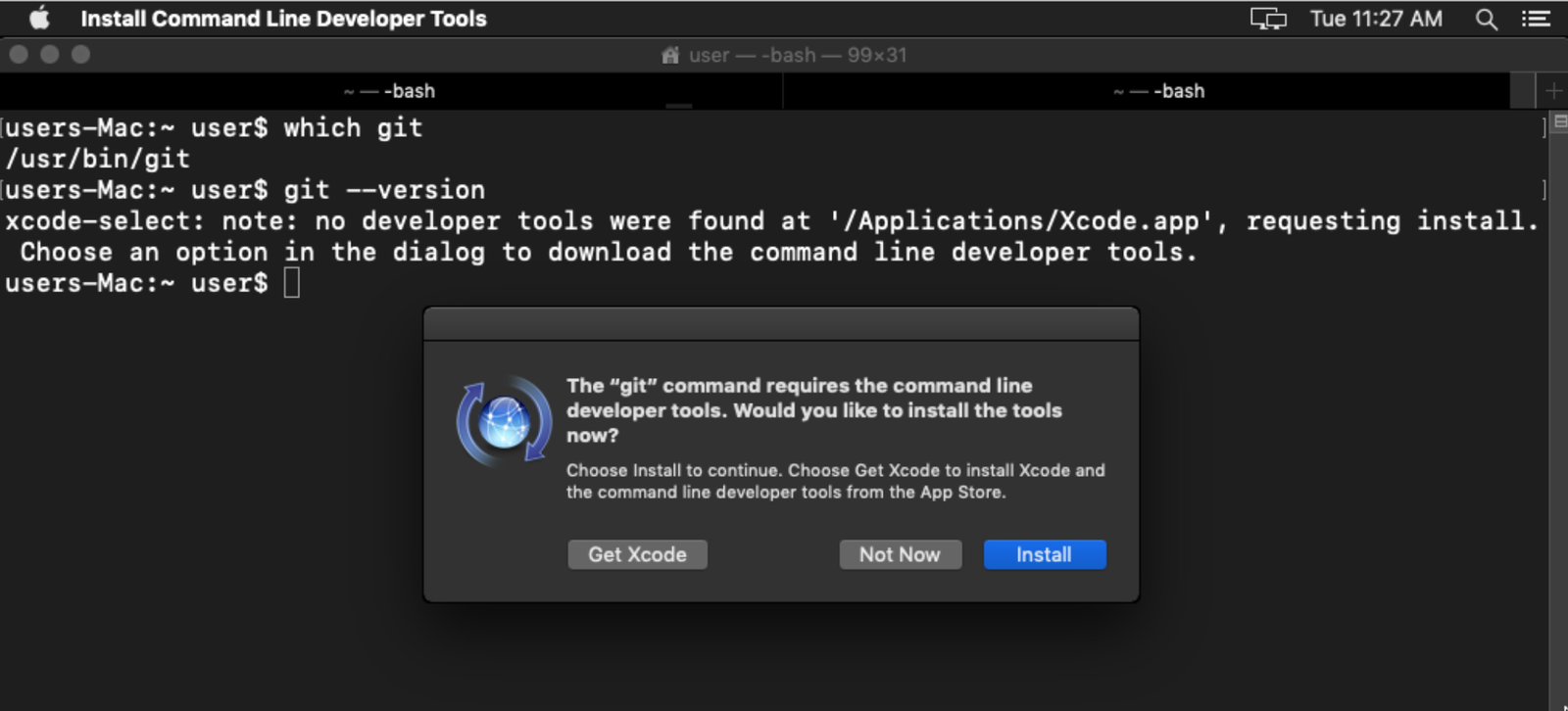
Trigger the Prompt: Open your Terminal application (found in
/Applications/Utilities/) and run any command that requires the tools, such asgit --versionormake. Alternatively, you can directly request the install dialog with the command:xcode-select --installThe Pop-up Dialog: Almost immediately, a software update dialog will appear on your screen. It will have a title like “The
xcode-selectcommand requires the command line developer tools. Would you like to install the tools now?”Install: Click on “Install” to agree. You will need to accept Apple’s software license agreement. The download, which is about 1.2 GB, will begin automatically.
Wait for Completion: The installer will download and set up the packages without any further input. This process can take several minutes depending on your internet speed.
Verify: Once completed, you can verify the installation by checking the version of one of the included tools, for example:
git --version # Output should be something like: git version 2.37.0 (Apple Git-136) clang --version # Output should show the Apple clang version number.
This method is ideal for the vast majority of users. It’s straightforward, managed by Apple, and ensures you get the correct version of the tools for your operating system.
Method 2: Manual Download from Apple Developer
For users who may have issues with the pop-up installer or who need to download the package for offline installation or system administration purposes, manually downloading the package from the Apple Developer website is an excellent alternative.
Navigate to the Developer Downloads Page: Go to developer.apple.com/downloads/all/. You will need to sign in with your Apple ID. (A free account is sufficient).
Search for Command Line Tools: In the search bar, type “Command Line Tools for Xcode.”
Select the Correct Version: Find the version that corresponds to your macOS version. Apple typically only lists the latest version, which is compatible with the current and recent macOS releases.
Download: Click the download button next to the correct package (
.dmgfile).Install: Once the download is complete, open the
.dmgfile and run the installer package (.pkgfile) inside. Follow the on-screen instructions.Verify: After installation, verify it was successful using the terminal commands mentioned in Method 1.
Method 3: Installation via Xcode (The Comprehensive Route)
If you plan to do iOS, iPadOS, macOS, or watchOS app development, you will need the full Xcode application. Installing it will also satisfy the xcode-select: note: install requested for command line developer tools requirement, as the CLT are bundled within it.
Open the Mac App Store: Search for “Xcode.”
Download and Install: Click “Get” and then “Install.” Be warned: Xcode is a very large download (over 20 GB) and will take significant time and disk space.
Open Xcode Once: After installation, it is crucial to open Xcode once.
Accept the License: You will be prompted to accept the software license agreement and allow Xcode to perform some first-time setup, which includes installing the components needed for the command-line tools.
Verify: You can verify the installation from the terminal as before.
Advanced Management: Using xcode-select
Once you have multiple versions of the developer tools installed (e.g., CLT for the stable macOS and a beta version of Xcode), you can use the xcode-select command to switch between them.
Check the Current Active Developer Directory:
xcode-select -pThis will print the path to the currently selected tools, e.g.,
/Library/Developer/CommandLineToolsfor the standalone CLT.Switch to a Different Toolchain: If you have the full Xcode app installed and want to use the tools inside it, you can point
xcode-selectto it.sudo xcode-select -s /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer
Use
sudoand provide your administrator password. You can specify the path to a beta version of Xcode (e.g.,Xcode-beta.app) if you have one.Reset to the Default: If you ever need to reset the selection to the system default (which will point to the standalone CLT if installed, or trigger the install request if not), use:
sudo xcode-select --reset
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after installation, you might run into problems.
“xcode-select: error” After Installation: If you still get errors after a seemingly successful install, the active developer directory path might be incorrect. Use
xcode-select -pto check it. If it’s pointing to a non-existent directory, usesudo xcode-select --resetto fix it.License Agreement Not Accepted: The tools will not work until you accept Apple’s license. The GUI installers handle this automatically. If you need to accept it via the terminal (e.g., on a headless server), you can use:
sudo xcodebuild -license
Press the
spacebarto scroll through the agreement and typeagreeat the end to accept.Verification is Key: Always use
git --versionor a similar command to verify the tools are active and working after any installation or change.
Conclusion: From Prompt to Power
The message xcode-select: note: install requested for command line developer tools is a rite of passage for every macOS developer. Far from being a troublesome error, it is a helpful and automated guide that ensures you have the foundational elements needed to build software. By understanding what it means and following the straightforward installation methods outlined in this article, you transform this prompt from a roadblock into the first step of your development journey. Whether you choose the lean Command Line Tools or the full-featured Xcode IDE, you are now equipped to resolve this prompt confidently and manage your development environment effectively. Your terminal is now ready for action.





Comments 1